Glossary
This page has been deprecated and no longer updated. Removal is planned for early July 2025. Please refer to the new IoT Glossary.
APN
Access Point Name
A gateway between a GSM, GPRS, 3G, or 4G mobile network and another computer network, usually the public Internet.
The APN needs to be configured on the device. For emnify, it's em or emnify.
Application token
A unique identification key used to authenticate emnify's APIs. Also used when authenticating the OpenVPN service.
A2P SMS
Application-to-Peer SMS
The SMS sent and received between an application and a device (or vice versa).
Learn more about the SMS types supported by the emnify platform and how to Receive MO SMS via API callback.
Assigned SIM
SIM that has been assigned to a device.
AT+CREG AT command
Gives information about the registration status and access technology of the serving cell.
AuC
Authentication Center
A part of GSM infrastructure, validates any SIM card attempting network connection when a phone has a live network signal.
BIC
Batch Identification Code
A unique code for ordered SIM cards used to register the SIM cards in the SIM Inventory.
BS
Base station
A fixed transceiver that acts as the primary hub for communication with one or more wireless mobile devices. It serves as the central point for wireless devices to connect and communicate within its coverage area.
A satellite base station is a variant that extends this functionality through satellite links, enabling it to transmit and receive signals to and from orbiting satellites. Unlike standard base stations, these connect with satellite ground stations and other communication networks through the ground core network, providing service in remote areas where terrestrial connectivity is limited or unavailable.
Callback URL
URL that will be called by a service to send and receive data related to an event that caused this action.
Carrier-agnostic network
A network that doesn't limit or prefer any specific network in a country and establishes a connection over any network that's transparent to the device.
Check digit
A checksum appended to identification data (for example, IMEI, EID, or ICCID) representing the preceding digits and calculated using an algorithm.
Check digits are used to validate the identifier, verify data integrity, and help prevent errors in equipment databases.
Several identifiers have a check digits but can be calculated differently and have different names. For example, ICCID numbers use a Luhn checksum digit, while the last digits of the EID are called check digits.
Connectivity status
This is the connectivity status of a device. It can be set to:
| Status | Portal Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Online |
| Device is transmitting or can transmit data through a data tunnel. |
| Attached | Device is attached to a network but hasn't established a data tunnel. | |
| Offline | Device isn't attached to a network. | |
| Blocked | Device isn't permitted to perform any actions. |
Coverage policy
Referred to as Tariff Profile in the API
A policy that defines which networks or countries SIM should operate in.
CSM
Customer success manager
A member of emnify's team dedicated to helping you grow and achieve your goals. For a full explanation of the role, see Support.
Data RX
Data received by the device.
Data session
A session between opening and closing a data connection to the network.
Data TX
Data transmitted by the device.
Data usage
The data that has been used by a device, both transmitted and received.
DDoS
Distributed Denial of Service Attack
An attack where the attacker sends multiple requests to a web resource with the aim of exceeding the website’s capacity to handle multiple requests and prevent the website from functioning correctly.
Default Workspace
The Workspace that automatically loads when a user logs into the emnify Portal. This is set individually per user and doesn't affect other users in the organization. For most users, the first Workspace you were invited to is your default.
You can only log in to your default Workspace initially, but you can switch to other accessible Workspaces using the Workspace switcher.
Device status
Referred to as Endpoint status in the API
Reflects the current state of the device and determines whether a device can connect to a network or incur charges.
Learn more about the different device statuses and how to configure them in the emnify Portal.
DNS
Domain Name System
A hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network to map a hostname to an IP address.
Dynamic IP
An IP that changes over time.
EARFCN
E-UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number
A numbering system used in LTE networks to identify specific radio channels for transmitting and receiving data. The number, always an integer, ranges from 0 to 65535. It helps determine the exact carrier frequency used for uplink (sending data from mobile devices to the network) and downlink (sending data from the network to mobile devices). The EARFCN is independent of the channel bandwidth, simplifying frequency selection to enhance device connectivity without interference.
eDRX
Extended Discontinuous Reception
A device configuration that specifies the periodicity in which the device listens for incoming data on the radio. Instead of using a periodicity of 2.56 ms (DRX) it can be increased up to 40 minutes, thus reducing power consumption.
EID
eUICC Identifier
The eUICC Identifier (EID) provides a unique global serial number for an eUICC. It has a fixed length of 32 digits, as indicated in the following diagram:
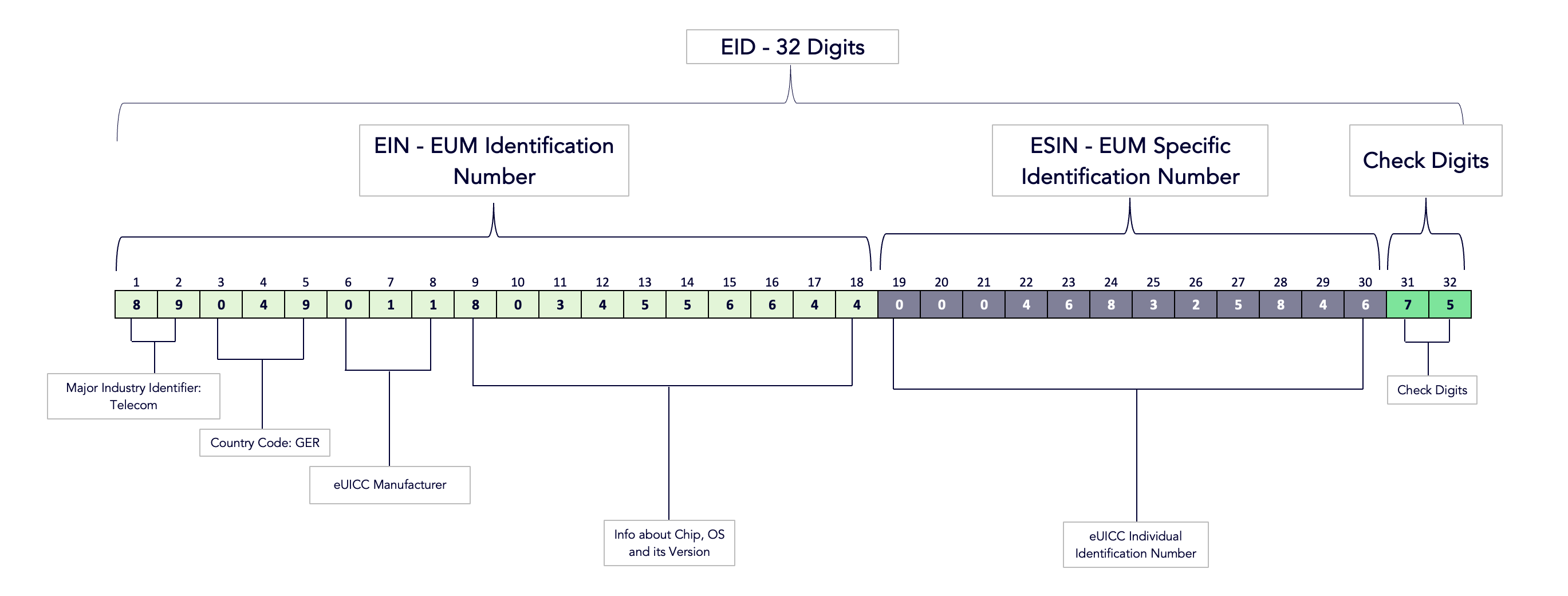
The EUM specific identification number (ESIN) and check digits are for example purposes only, and the values aren't real.
Unlike the ICCID, the EID remains the same throughout the life of the eSIM. Therefore, you can use it as a permanent identifier to keep track of your SIM cards.
Endpoint
A representation of the device which has a SIM installed. Often used as a legacy term for a device, particularly in the REST API.
eSIM
Embedded SIM
Because of the "e" (for embedded) in its name, eSIM is sometimes incorrectly used for referring to the MFF2 physical form factor of an eUICC chip that's designed to be permanently surface-mounted inside a device. Within the IoT industry, eSIM refers to the entire solution that's comprised of an eUICC-equipped SIM along with the software platform for OTA provisioning. Although eSIMs can be embedded directly in a device, they're also manufactured as pluggable SIM cards. The emnify eSIM has capabilities not available with other eSIMs.
eUICC
Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card
The embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC) is a component of a SIM card. It allows consumers and IoT manufacturers to provision the SIM with a new mobile network operator (MNO) profile over-the-air.
Learn more about the eUICC in the blog post: What is an eUICC and why does it matter?
Event log
A log that stores all device events.
Form factor
The form factor of a SIM card represents the SIM card format. SIM cards vary in size (Mini vs. Micro vs. Nano), function (embedded vs. standard), and quality (industrial grade vs. standard):
- 2FF: Mini SIM card
- 3FF: Micro SIM card
- 4FF: Nano SIM card
GEO
Geostationary equatorial orbit
A type of orbit situated approximately 35,786 kilometers above the Earth's equator, perfectly aligned with the planet's rotation. Satellites in this circular orbit synchronize with the Earth's rotational period, appearing stationary in the sky from any fixed point on the ground. This characteristic makes GEO especially valuable for telecommunications satellites, as they consistently cover the same area on the planet's surface. This facilitates continuous communication without the need for tracking movement across the sky.
GGSN
Gateway GPRS Support Node
Part of the GSM infrastructure, the GGSN is responsible for the interworkings between the GPRS network and external packet switched networks.
Globally distributed infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure that's distributed globally, with several local breakout points for better traffic handling.
GNSS
Global navigation satellite systems
Comprises several satellite constellations, including GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (European Union), BeiDou (China), and QZSS (Japan). These systems, together with ground control stations and receivers, provide global coverage for precise location and time information. GNSS is crucial for navigation and positioning in various applications, from mobile apps to transportation.
emnify specifically utilizes the GPS constellation for its operations.
GSM
Global System for Mobile Communications
A standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute to describe the protocols for second-generation digital cellular networks used by mobile devices.
HAPS
High-altitude platforms
Vehicles, such as planes or balloons, stationed in the stratosphere. They're typically at an altitude of 20 kilometers, higher than conventional aircraft but lower than satellites. Operating similarly to satellites, HAPS provide continuous surveillance or communication services over a specific area, offering proximity, coverage, and flexibility advantages.
HLR
Home Location Register
A database from a mobile network in which information from all mobile subscribers is stored. Part of GSM infrastructure.
HTTP POST request
A request method supported by the HTTP protocol, which typically includes data in the request body.
IC
Integrated Circuit
A semiconductor chip containing a large number of extremely small electronic components. For example, a CPU, the chips on computer memory cards, the electronic part of a SIM card, an eUICC, etc.
ICCID
Integrated Circuit Card Identifier
The integrated circuit card identifier (ICCID) is a 20-digit code used to identify a SIM card. It includes a SIM card's country, home network, and identification number, as indicated in the following diagram:
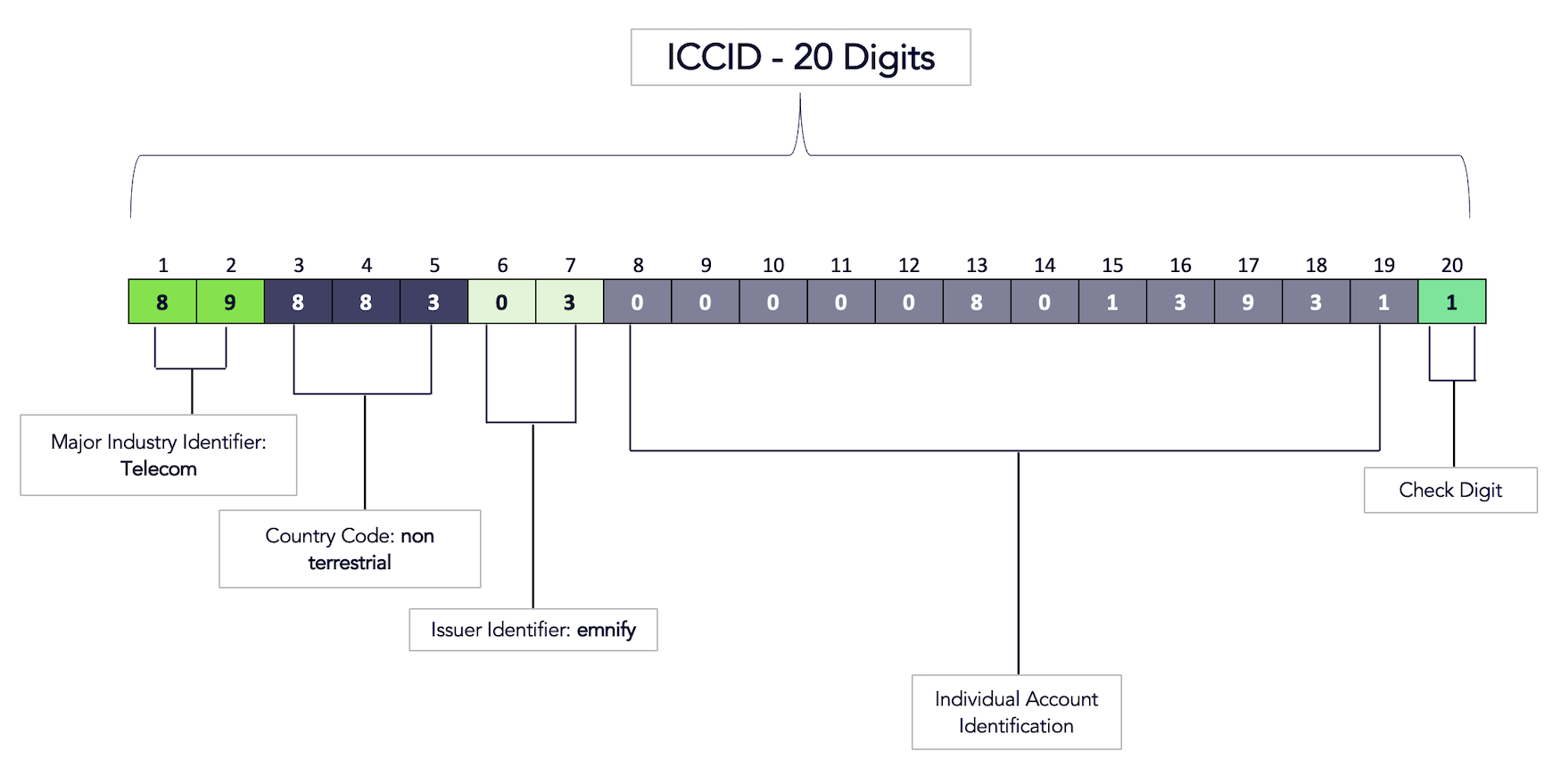
Following the introduction of eUICC SIM cards in 2021, there are situations where the ICCID can no longer be unique. For example, the ICCID value can change when a different SIM profile is provisioned on the eSIM.
The emnify REST API returns two ICCID values: iccid and iccid_with_luhn.
The iccid_with_luhn value includes the final Luhn checksum digit, while the iccid value doesn't.
API references: SIM object and Endpoint object
IMEI
International Mobile Equipment Identity
A unique number used to identify cellular modems. There are two types of IMEI numbers referenced by the emnify system:
- IMEI: 15 digits including the final check digit.
- IMEI Software Version (IMEISV): 16 digits composed of the first 14 digits of the IMEI plus two additional digits that represent the Software Version Number (SVN).
The IMEI consists of the following elements:
- Type Approval Code (TAC): Eight digits, identifies the cellular device by providing information about its manufacturer and model.
- Serial Number (SNR): Six digits, uniquely identifies the device against others with the same TAC.
- Check digit: One digit, represents the preceding digits and is calculated using an algorithm.
In some contexts, the IMEISV is used instead of the IMEI.
For example, when retrieving device information through the Endpoint API, the imei value in the API response is the 16-digit IMEISV, while the imei_with_luhn returns the 15-digit IMEI with the check digit.
For more information, see Why my device's IMEI is different in the emnify Knowledge Base or the Endpoint Object API reference.
IMEI lock
The practice of strictly associating a SIM to the device with a certain IMEI number. For more information, see the IMEI lock feature description.
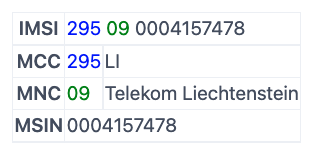
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
A unique number used to identify a GSM subscriber. Therefore it changes if a device connects to a different operator while roaming.
See how the IMSI is constructed
An IMSI is usually a 15-digit number but can be 14 digits in some cases. It comprises three components: MCC, MNC, and MSIN.
MCC: 3-digit country identifier
MNC: operator identifier (two or three digits)
MSIN: identifier for the connected device (nine or 10 digits)
IPsec
A protocol suite for Secure Internet Protocol (IP) communications that works by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session.
IP subnet
A logical subdivision of an IP network.
JSON
JavaScript Object Notation
A lightweight format for storing and transporting data. It's often used when data is sent from a server to a web page.
LAC
Location Area Code
A unique 16-digit fixed-length location area identity code that identifies a phone number’s location area.
LEO
Low Earth orbit
The region of space close to the Earth, typically between 500 and 2,000 kilometers. Satellites in LEO orbit the Earth rapidly, completing multiple orbits each day, which makes them ideal for telecommunications due to their proximity to the planet. This close range allows for lower latency in communications and detailed imagery capture.
Linked Workspaces
Two or more Workspaces connected under a single main organization, allowing centralized user management while maintaining separate configurations and billing.
For setup instructions, see Link existing Workspaces.
Luhn checksum digit
A check digit calculated from the previous digits using the Luhn algorithm.
Main organization
The primary organization that holds the contract with emnify and oversees linked Workspaces. It determines which user is assigned the SuperAdmin role for managing multiple Workspaces.
Unlike a traditional sub-account structure, the main organization doesn't automatically inherit permissions across linked Workspaces beyond the SuperAdmin role.
MDOP
Modem device operational parameters
Configurable settings and statuses within a modem that dictate its functionality and performance. In satellite connectivity, these parameters are crucial for optimizing the modem's operation to handle the unique challenges of satellite communications, such as variable signal strength, higher latency, and bandwidth constraints.
MEO
Medium Earth orbit
A range of orbits around Earth positioned between low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary equatorial orbit (GEO). Satellites in MEO typically orbit at altitudes of about 7,000 to 25,000 kilometers. This orbit is commonly used for navigation satellites, like those in GPS, because it balances coverage area and signal delay well.
MFA
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires you to provide two or more pieces of evidence (also known as factors) to verify your identity before accessing a website or application. MFA is sometimes called two-factor authentication (2FA) and has historically been at emnify.
To learn more about MFA and how it's enforced at emnify, see the Set up multi-factor authentication guide.
MFA key
Multi-Factor Authentication key
A combination generated by an external device or a service that's used to authenticate the user during the multi-factor authentication (MFA) process. These keys are sometimes referred to as "codes" or "tokens."
MSISDN
Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number
A unique number used to identify a mobile phone number internationally—essentially the telephone number assigned to each SIM. For an emnify IoT eSIM, this number is needed for its ability to receive SMS messages.
emnify's system distinguishes application-to-peer (A2P) SMS from peer-to-peer (P2P) SMS based on the length of the source (SMS MO) or the destination (SMS MT) address.
- If there are 7 digits or less (that is, an invalid MSISDN), an SMS will be considered A2P.
- If there are 8 digits or more, an SMS will be processed as MSISDN and will be considered P2P.
MSC
Mobile Switching Center
The part of GSM architecture that controls the network switching subsystem elements.
NB-IoT
Narrowband IoT
A low-power wide-area network technology that offers robust IoT connectivity. It's designed for applications in remote areas or inside buildings where signal strength can be a challenge. NB-IoT features low power consumption and reduced module costs, making it an ideal choice for devices that operate for long periods without frequent battery replacements or recharging. For more information, see LPWAN: LTE-M/NB-IoT radio access technology (RAT) type.
NOC
Network operations center
A centralized location where administrators supervise, monitor, and maintain a telecommunication or satellite network. The emnify NOC is used primarily for incident management.
NTN
Non-terrestrial networks
A type of network that isn't based on terrestrial infrastructure. In the context of emnify's services, it specifically refers to the Skylo satellite IoT network. This satellite network is part of emnify's IoT SuperNetwork SatPlus, providing global connectivity by combining terrestrial and satellite coverage.
NTN-IoT
NB-IoT over NTN
A standardized cellular technology that defines the way satellites provide direct-to-device telecommunication services with NB-IoT cellular modems. NTN-IoT works similarly to NB-IoT devices, except the device telemetry data is sent through a satellite communication channel.
Organization
A business entity (company, subsidiary, branch, or department) associated with a Workspace. Each organization has its own billing, user management, and contract with emnify.
For details, see Workspace settings.
OTA
Over-the-Air
A method of wireless distribution of the software, configuration settings, or encryption keys.
OTA provisioning
A technology that allows changes to the SIM memory over-the-air.
OpenVPN
An open source software application that implements virtual private network (VPN) techniques for creating secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities.
emnify hosts an OpenVPN service that allows you to establish a private network between a device and any remote client location.
P2P SMS
Peer-to-Peer SMS
SMS sent from a device with any SIM to a device with the emnify SIM.
Learn more about the SMS types supported by the emnify platform and P2P routing via the emnify REST API.
PDP context
Data structure present on both the serving GPRS support node (SGSN) and the gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), which contains the subscriber’s session information when the subscriber has an active session.
Private IP
An IP address that's not reachable from the public Internet but only through a local or virtual network. Dynamic private IPs keep changing, whereas static private IP addresses don't change.
PSM
Power Saving Mode
While in power saving mode (PSM), the device tells the network that it's powering off for a specific time and sending periodic updates in longer-than-usual intervals. When the device comes back online, it doesn't need to reattach to a network but can use an already-created PDP context, thus saving power.
Public IP
An IP address accessible from the public Internet.
RAT
Radio access technology
The specific technology used to wirelessly connect a device to a network. It plays a crucial role in cellular communication and IoT connectivity. Different types of RATs, such as 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, LTE-M, and NB-IoT, cater to various use cases based on their unique characteristics and capabilities. For more information, see radio access types.
RESTful API
The representational state transfer application programming interface allows you to integrate services with your applications.
RTT
Round-trip time
The time it takes for a signal to travel from a source to a destination and back again, typically measured in milliseconds (ms). This measure includes both the transmission time to the destination and the time for an acknowledgment or response to return to the original sender.
While RTT measures the total time for a signal to travel to a destination and back, latency refers only to the one-way delay from the source to the destination.
SASE
Secure Access Service Edge
SASE is a term coined by Gartner which combines software-defined networking (SDN) and security and serves it as cloud-based Security-as-a-Service.
SDN
Software-Defined Networking
An approach that allows network administrators to programmatically initialize, control, change, and manage network behavior dynamically via open interfaces.
Service profile
A profile that defines the services and capabilities of a device managed through the emnify platform.
SIB
System Information Block
Integral components in cellular networks, specifically used within 3G, 4G (LTE), and 5G technologies. SIBs contain essential information that mobile devices need to operate effectively on a network. This information is broadcast by the base stations (cell towers) and includes a variety of operational parameters about the network.
In satellite connectivity, SIBs are data sets broadcast by satellites to deliver crucial operational parameters like beam coverage, frequency bands, and handover guidelines. These blocks facilitate device configuration and communication efficiency, addressing the unique challenges and high latencies of satellite networks.
SIM
Subscriber Identification Module
A subscriber identification module (SIM) contains an integrated circuit (IC) that's often mounted on a plastic card. Pluggable SIMs mounted on plastic cards are offered in various form factors. A SIM stores data used to identify a subscriber (IMSI) along with other network information for connecting and authenticating with a mobile network operator (MNO). See also eSIM - Embedded SIM.
SIM batch
A collection of SIM cards that can be registered with a single BIC code.
SIM hosting fee
Monthly fee for an activated SIM.
SIM profile
The mobile network operator (MNO) ID information stored in the SIM's memory.
SIM registration
A process to allow your SIM cards to be registered within your Workspace and visible in the SIM Inventory.
SIM status
Reflects the current state of the SIM in the SIM lifecycle.
SMPP
Short Message Peer-to-Peer
A protocol used by the telecommunications industry for exchanging SMS messages between short message service centers (SMSC) and/or external short messaging entities (ESME).
SMS console
An interface to send A2P SMS from the platform to the SIM card.
SMS firewall
A firewall that controls the SMS flow.
SMS MO
Mobile originated SMS
SMS sent from the device with the emnify SIM.
Learn more about the SMS types supported by the emnify platform.
Using the emnify REST API, you can dispatch MO SMS from devices as HTTP POST requests toward a user-configurable URL.
For more information, see Receive MO SMS via API callback
SMS MT
Mobile terminated SMS
SMS that are received by a device with an emnify SIM.
Learn more about the SMS types supported by the emnify platform.
Source address
The address of the SMS sender as displayed on the receiving device.
Source Workspace
The Workspace where a SIM card is currently assigned before being transferred to another Workspace. During a SIM transfer, the source Workspace is responsible for all usage and subscription charges accrued up to the exact moment of transfer. After the transfer, billing and management shift to the target Workspace.
For details, see Transfer SIMs between Workspaces.
Static IP
An IP that doesn't change over time.
TA
Timing advance
A control mechanism used in mobile communications to adjust the timing of signals sent from a mobile phone to a base station. This adjustment ensures that the signal arrives at the correct time, avoiding interference with signals from other users.
TAC
Timing advance command
A directive issued by a base station in cellular networks to adjust the timing of data transmissions from mobile devices, ensuring signals arrive precisely and avoid interference. In satellite connectivity, TAC is critical for managing the greater transmission delays due to the significant distances signals travel.
Target Workspace
The Workspace that receives a SIM card during a transfer. Once a SIM is transferred, all new usage, subscription fees, and data allowances are billed to the target Workspace. The SIM remains in the target Workspace unless transferred again.
For details, see Transfer SIMs between Workspaces.
Traffic pooling
A term used to describe the service model when various devices utilize the same data pool.
UE
User equipment
Devices end-users use to communicate with a network, such as sensors and other IoT devices.
Unassigned SIM
SIM that has been unassigned from a device.
URC
Unsolicited result code
Notifications automatically sent from a device to report status changes or specific events, such as changes in network registration. These codes are generated without a direct request and can differ in format from standard AT command responses. URCs are crucial for real-time monitoring and managing device states in a network.
Usage limit
User-defined limit of consumption for a certain service (data, SMS) per device.
User account
An account associated with a specific person and used to log in to one or more Workspaces. User accounts can be assigned a role (for example, Administrator) per Workspace.
A user can have different roles in different Workspaces. For more information, see Roles and permissions.
User-defined coverage
An ability to select which network the customer's SIM connects to.
User-defined networking
An approach that enables users to create their own virtual mobile network, define service and security policies, and provision coverage policies and data packages.
VPC
Virtual Private Cloud
A secure private cloud hosted within a public cloud where you can host websites, store data, run applications, etc.
VPN
Virtual Private Network
A service that protects your internet connection and privacy online.
IPsec and OpenVPN are both protocols for securing data transmission through a VPN.
For more information, see IPsec vs OpenVPN: What's the difference?
Workspace
An independent entity in the emnify Portal used to manage IoT connectivity. Each Workspace has separate configurations, billing, and user roles. Organizations can operate multiple linked Workspaces to support independent business units, product lines, or test environments.
By default, each emnify account includes one Workspace, with additional Workspaces available for accounts with the Pro Package.
For more information, see Multiple Workspaces.
Workspace switcher
A feature in the emnify Portal that allows users with the appropriate roles to switch between Workspaces without logging out. This is useful for managing multiple Workspaces under a single account.
For instructions, see Switch between Workspaces.