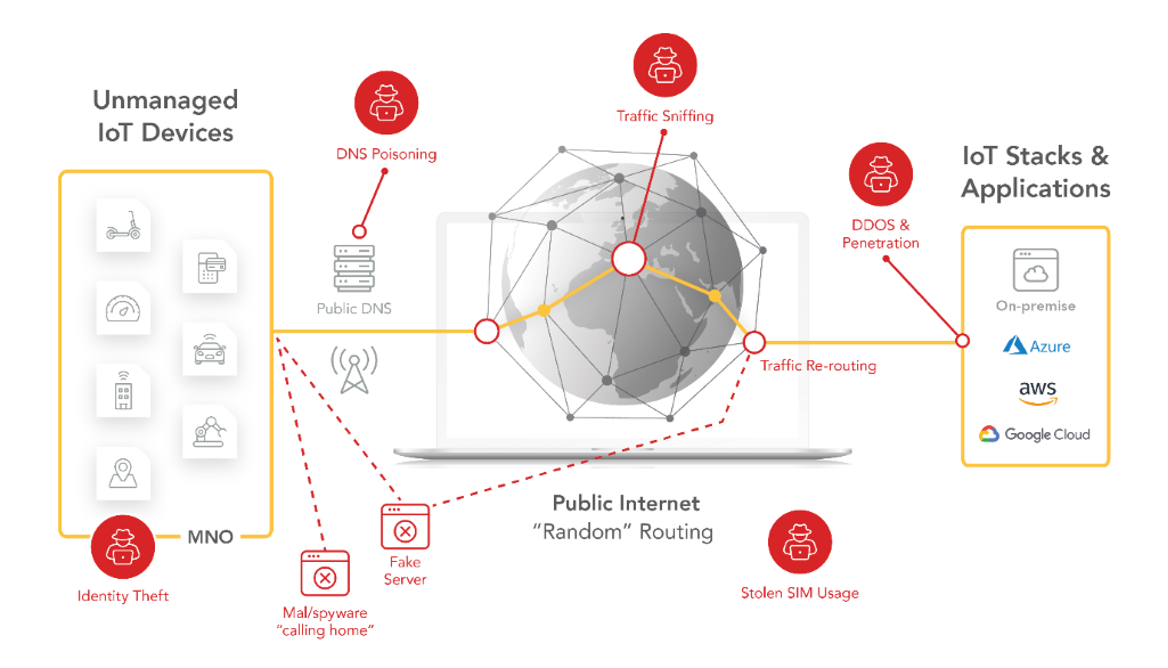
Security
Given the globally distributed nature of the devices, smaller footprints and lack of resources, it can get difficult to individually secure IoT devices.
emnify uses a SASE approach to simplify securing devices—using several services specifically to protect customer data, filtering malicious content and preventing unauthorized access.
Why does IoT require SASE?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) introduces a new architecture where networking and security functions are bundled in a cloud-delivered service. This approach allows you to apply consistent security standards to all your devices independent of the location. Additionally, it enables the integration of security features right from the start.
Key features of SASE for IoT architecture include:
- Dynamic Data Routing with Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN)
emnify utilizes a SD-WAN to route data to the closest cloud region using the Regional Breakout concept. This enhances latency and data stability, ensuring that data remains within the designated continent and jurisdiction. - Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
emnify offers centralized policy definition for devices, including networks that can be accessed and authorized IP addresses for remote device access. All configurations are managed through the central platform and applied wherever the device is.
Security features
The following sections delve into some of the security features offered by emnify.
DNS
When a device establishes a connection, it uses a Domain Name Service (DNS) server to resolve a hostname to an IP address for data transmission.
For example, a hostname like iot.example.com is mapped to an IP address like 192.0.2.1.
Cellular providers typically provide DNS services.
By default, emnify routes all DNS queries over Google’s public DNS 8.8.8.8.
Some devices and modules allow you to configure the DNS service.
For example, Quectel uses the AT+QIDNSCFG command, while SIMCom uses the AT+CDNSCFG command.
Configuring the DNS service is beneficial for using your own or private DNS servers, enhancing security and control.
Customers can also configure to use their own DNS, no matter if it’s a public or a private one. For more information, see Configure DNS settings.
IMEI lock
Device manufacturers often face issues related to SIM card theft, as pluggable SIM cards can be removed from a device and used for free internet access. The IMEI lock feature prevents using SIM cards on any other device by binding the SIM to a specific international mobile equipment identity (IMEI), which serves as a unique device identifier.
When the automatic IMEI lock is configured, the emnify platform binds the SIM cards to the first device that establishes a data connection. All future device connections are restricted to this specific device.
However, emnify also provides a clear IMEI lock function, which allows you to remove the IMEI lock when necessary. You can access this action through the emnify Portal’s Connected Devices. While this provides flexibility for legitimate use cases such as device replacement or troubleshooting, it should be used cautiously as it also removes the security measure preventing unauthorized SIM usage.
Multi-factor authentication
As of March 2024, MFA is mandatory for all non-trial emnify Portal accounts to proactively safeguard our IoT ecosystem and meet regulatory security compliance. For more information and configuration instructions, see Set up multi-factor authentication.