IoT Satellite SuperNetwork
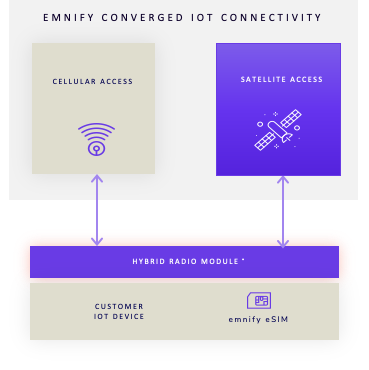
emnify has developed a converged satellite and cellular service solution that helps reduce IoT connectivity complexity in areas without terrestrial cellular connectivity. By aggregating and complementing traditional cellular IoT connectivity with outdoor satellite NB-IoT over non-terrestrial networks (NTN-IoT) connectivity, emnify maximizes global IoT service coverage—using a single SIM card.
Satellite NTN-IoT connectivity can serve as a fallback solution when terrestrial cellular connection drops out. Alternatively, it can be the sole means of connection for stationary use cases, enabling data transport in remote areas.
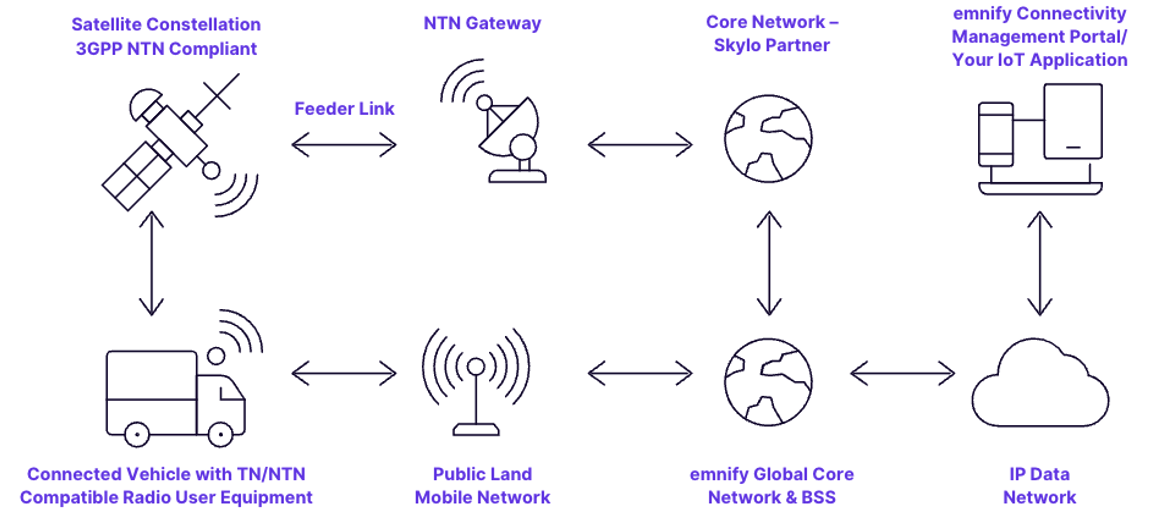
The integration with Skylo enables emnify to offer terrestrial cellular and satellite NTN-IoT data service through a single IoT connectivity management and billing platform.

Available satellite products
To get started with satellite NTN-IoT connectivity, you need the following:
- emnify satellite eSIM
- Satellite-capable data plan (SatPlus, SatSolo, CellSolo)
- A compatible device
- Available network coverage
emnify Satellite eSIM
With an emnify satellite eSIM, businesses can connect, integrate, operate, and secure thousands of devices to terrestrial cellular and non-terrestrial networks (NTN). It allows enterprises to expand their IoT business into new geographies and use cases, enabling seamless IoT connectivity for increased device uptime.
The emnify satellite eSIM is a product different from the standard SuperNetwork IoT eSIM. The emnify satellite eSIM uses a single International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and allows you to connect to the Skylo satellite network and cellular networks worldwide. Having only one IMSI means the emnify satellite eSIM can connect to fewer networks than the SuperNetwork IoT eSIM.
The satellite eSIM is a machine-to-machine (M2M) embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC) compliant with SGP.01, SGP.02, and SGP.016. It’s available in four form factors: 2FF, 3FF, 4FF, and MFF2.
See the SuperNetwork IoT eSIM reference documentation for a description of an M2M eUICC, form factor specifications, and more.
Satellite data plans
SatPlus
The SatPlus data plans are a converged offering for mobile devices that move in and out of cellular coverage and need a fallback mechanism to satellite connectivity.
Three SatPlus plans are available: SatPlus 10, SatPlus 30, and SatPlus 60.
The SatPlus data plan is a postpaid plan that charges monthly per active SIM. You can suspend SIMs anytime, and there are no activation or reactivation fees.
emnify bills satellite messages in increments of 100 bytes and rounded up to the next increment if necessary. For example, two messages are deducted from the allowance if a data transmission packet exceeds 100 bytes but is below 200.
The first message includes an IP/UDP overhead of 28 bytes, so you can only send 72 bytes of payload with the first message. The maximum packet size is 256 bytes.
Satellite and cellular messages are pooled. For example, a fleet of 10 devices with a SatPlus 30 plan can consume 300 satellite messages and 100 MB of cellular data per month without additional charges.
SatSolo
The SatSolo data plan is offered for stationary devices deployed in locations without cellular coverage. Based on the average data consumption, the SatSolo postpaid plans can be tailored from 1 KB to 500 KB monthly. A pooled and non-pooled option is available.
SatSolo plans are charged based on volume without activation or reactivation fees. Every data packet is invoiced at a minimum of 50 bytes, including the initial IP/UDP overhead of 28 bytes. After 50 bytes, emnify charges per byte. For example, a payload of 8 bytes, resulting in a message size of 36 bytes, is billed as a 50-byte data transmission. However, a payload of 50 bytes, resulting in a message size of 78 bytes, is billed as a 78-byte transmission.
CellSolo
The CellSolo plan is offered for stationary devices using emnify satellite eSIMs. This data plan is beneficial if it’s not clear whether the device will have cellular or only satellite coverage. If cellular coverage is available at the deployment site, then a CellSolo data plan is used. If not, then it uses SatSolo.
CellSolo provides different network coverage than the standard cellular plans. Since the plan is built for satellite connectivity, it includes networks with only LTE-M, NB-IoT, and 2G coverage.
Coverage for satellite products
Modules that support satellite connectivity typically only offer 2G, LTE-M, and NB-IoT cellular connections. Additionally, the satellite eSIM only includes one IMSI. This results in the satellite coverage being different from the cellular SuperNetwork coverage.
The following table shows the number of cellular networks available in each country and whether satellite coverage is available.
| Country | # of networks | Satellite available |
|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 1 | No |
| Algeria | 2 | No |
| Andorra | 1 | No |
| Angola | 1 | No |
| Argentina | 1 | No |
| Australia | 0 | Yes |
| Austria | 2 | Yes |
| Bangladesh | 1 | No |
| Belarus | 2 | No |
| Belgium | 3 | Yes |
| Belize | 1 | No |
| Benin | 2 | No |
| Bolivia | 1 | No |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 2 | No |
| Botswana | 1 | No |
| Brazil | 1 | Yes |
| Bulgaria | 3 | Yes |
| Burkina Faso | 1 | No |
| Cameroon | 1 | No |
| Canada | 1 | Yes |
| Chad | 1 | No |
| Chile | 2 | No |
| Colombia | 1 | No |
| Comoros | 1 | No |
| Congo | 2 | No |
| Croatia | 2 | Yes |
| Cyprus | 3 | Yes |
| Czech Republic | 1 | Yes |
| Democratic Republic of Congo | 2 | No |
| Denmark | 2 | Yes |
| Dominican Republic | 2 | No |
| Ecuador | 1 | No |
| El Salvador | 2 | No |
| Estonia | 3 | Yes |
| Faroe Islands | 2 | No |
| Finland | 2 | Yes |
| France | 2 | Yes |
| French Guiana / Saint Barthélemy | 1 | No |
| Gabon | 2 | No |
| Gambia | 2 | No |
| Germany | 1 | Yes |
| Ghana | 1 | No |
| Gibraltar | 1 | No |
| Guatemala | 1 | No |
| Guinea | 1 | No |
| Guyana | 1 | No |
| Honduras | 1 | No |
| Iceland | 3 | No |
| Indonesia | 1 | Yes |
| Ireland | 1 | Yes |
| Israel and Palestine | 1 | No |
| Italy | 1 | Yes |
| Kazakhstan | 2 | No |
| Kenya | 1 | No |
| Kiribati | 1 | No |
| Kyrgyzstan | 1 | No |
| Latvia | 2 | Yes |
| Liberia | 1 | No |
| Liechtenstein | 2 | No |
| Lithuania | 2 | Yes |
| Luxembourg | 3 | Yes |
| Macedonia | 1 | No |
| Madagascar | 1 | No |
| Malawi | 1 | No |
| Malta | 2 | Yes |
| Mauritius | 1 | No |
| Mayotte / Reunion | 1 | No |
| Mexico | 1 | Yes |
| Mongolia | 1 | No |
| Montenegro | 1 | No |
| Netherlands | 1 | Yes |
| New Zealand | 1 | Yes |
| Nicaragua | 1 | No |
| Niger | 1 | No |
| Nigeria | 3 | No |
| Norway | 1 | No |
| Pakistan | 2 | No |
| Panama | 1 | No |
| Paraguay | 1 | No |
| Peru | 2 | No |
| Philippines | 1 | No |
| Poland | 3 | Yes |
| Portugal | 1 | Yes |
| Qatar | 1 | No |
| Romania | 1 | Yes |
| Russia | 2 | No |
| Rwanda | 2 | No |
| Serbia | 1 | No |
| Seychelles | 1 | No |
| Sierra Leone | 1 | No |
| Singapore | 2 | No |
| Slovakia | 2 | Yes |
| Slovenia | 3 | Yes |
| South Africa | 2 | No |
| South Sudan | 1 | No |
| Spain | 2 | Yes |
| Sudan | 1 | No |
| Sweden | 2 | Yes |
| Switzerland | 1 | Yes |
| Taiwan | 3 | No |
| Tajikistan | 1 | No |
| Tanzania | 1 | No |
| Togo | 1 | No |
| Tunisia | 1 | No |
| Turkey | 1 | No |
| Uganda | 2 | No |
| Ukraine | 2 | No |
| United Kingdom | 1 | Yes |
| United States | 1 | Yes |
| Uruguay | 1 | No |
| Uzbekistan | 2 | No |
| Vietnam | 1 | No |
| Zambia | 2 | No |
NTN-IoT technology
NB-IoT over non-terrestrial networks (NTN-IoT) is a standardized cellular technology established in the 3GPP Release 17. It defines a way for satellites to provide direct-to-device telecommunication services with NB-IoT cellular modems. It can offer coverage anywhere in the world, as long as there’s an appropriate satellite overhead. It’s usually used for service continuity, to enable cellular coverage where it’s unfeasible through terrestrial networks (for example, in maritime or remote areas), as well as service ubiquity in various situations where the terrestrial network infrastructures aren’t available (economic reasons) or are out-of-order (earth disasters such as earthquakes, floods, etc.).
How NTN-IoT works
NB-IoT over NTN works very similarly to NB-IoT devices, except the device telemetry data is sent from the device to the eNB through a satellite communication channel.
Satellites could be:
Geostationary equatorial orbit (GEO) satellites
Satellites with circular orbits at 35,786 kilometers above the Earth’s equator and follow the direction of the Earth’s rotation.
An object in this orbit has an orbital period equal to the Earth’s rotational period and thus appears motionless at a fixed position in the sky to ground observers.
Non-geostationary satellites
Satellites (LEO and MEO) that orbit around the Earth and move across the sky.
A constellation of multiple non-Geostationary satellites is necessary to carry service as they move over the horizon, requiring handover management to ensure service continuity.
- Medium Earth orbit (MEO) satellites typically orbit at an altitude between 7,000 to 25,000 km.
- Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites typically at an altitude between 500 km to 2,000 km.
High-altitude platforms (HAPS)
HAPS are airborne vehicles, like planes or balloons, that watch over Earth from the stratosphere.
Operating like satellites but closer to Earth, typically at 20 km altitude, they float above conventional aircraft and can offer continuous coverage of the territory below.
emnify Satellite NTN partner: Skylo
For the first generation of satellite-converged IoT service, emnify has partnered with Skylo, which provides global roaming network access using GEO satellite constellations. Because of this, the following specifications only cover GEO satellites.
Supported radio access technologies
emnify’s satellite eSIMs and platform support all devices and modules using the following radio access technologies (RAT):
NB-IoT over NTN (RAT 17, GEO satellite)
NB-IoT over NTN (NTN-IoT) is also part of the 5G NTN standardization from 3GPP Release 17. This technology has been specified to meet the demand for satellite IoT use cases in the following areas:
- Reduced cost
NTN-IoT allows for mass deployments of satellite IoT or hybrid IoT devices that enable terrestrial cellular and satellite NTN-IoT connections. - Low power utilization
For battery-powered use cases that require years of operation, NTN-IoT supports power saving features, such as PSM and eDRX, for satellite connections. It also reduces the maximum transmission power compared to the proprietary radio user equipment most traditional satellite IoT providers use. - Wider coverage for rural and non-terrestrial use cases
NTN-IoT utilizes the Coverage Enhancement (CE) feature with more retransmissions to ensure data is delivered. - Small module size
This technology enables miniaturized device form factors for sensors or wearables.
According to the specification, NTN-IoT deploys in the following frequency bands. To deploy NTN-IoT in multiple countries and regions, the modules need to support the satellite operator frequency bands.
- B255 (1.6 GHz) L-band
- B256 (2.0 GHz) S-band
NTN-enabled NB-IoT modules come in different versions:
- NTN-IoT only
- LTE-M/NB-IoT/NTN-IoT combined
- LTE-M/NB-IoT/NTN-IoT with 2G eGPRS fallback
Currently, roaming for NTN-IoT service is only provided by a single operator: Skylo. That said, more operators are developing and launching NTN-IoT service capabilities to provide NTN-IoT access to their satellite network’s supporting features.
For more information, see emnify’s NTN-IoT coverage (listed as SAT).
Supported devices
Compatible radio user equipment
To use emnify’s satellite converged IoT service, radio user equipment has to fulfill the following minimum requirements.
Supported IP data protocols
emnify supports UDP/IPv4 data transport via Skylo NTN (geostationary satellite IoT service). Skylo currently permits a throughput of 20x messages per minute, each with a maximum transmission unit (MTU) of 256 bytes. Non-IP data delivery (NIDD) isn’t supported by emnify.
To establish a successful data connection using a module and SIM, set the Access Point Name (APN) to em or emnify.
Compatible IoT radio modules
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have announced a range of radio modules that support satellite NTN-IoT connections, which you can find in the following table. Nordic and u-blox are expected to release compatible modules in 2024.
Contact your preferred vendor to inquire about samples and estimated delivery timelines.
Skylo certification of user equipment
To ensure the best performance of devices, emnify’s partner Skylo has restricted network access to those certified through their certification program. This includes the use of certified modems and radio modules. For more information, see the Skylo Certification Program.