SMS
Short Message Service (SMS) uses the same basic technology on IoT devices as that employed with consumer mobile devices. However, in the context of IoT devices, there are more modes of SMS operation and use cases that provide additional capabilities.
Classifications
SMS P2P
Peer-to-peer (P2P) SMS describes the mode of sending SMS from one device to another.
For IoT devices, this poses a security threat. Anyone with the correct MSISDN can issue commands to the device since there isn’t any built-in authentication process.
P2P also isn’t suitable for IoT device use cases in which a device needs to update, interact, or transmit frequently because a device is limited to receiving only six SMS messages per minute in this mode.
SMS A2P
SMS application-to-peer (A2P) describes the mode of SMS data exchange between a device and an application. One example of this is sending SMS using the emnify Portal.
Unlike P2P, A2P lets you interact with multiple devices using an application. Because A2P SMS can be automated, you can interact with your devices at scale. It also tracks messages, which enables you to see when a message has been delivered.
SMS MO and MT
Because the costs of sending SMS from an IoT device are higher than the cost of receiving SMS, all SMS usage is logged as either SMS MO (sent) or SMS MT (received).
Using the emnify REST API, you can dispatch SMS MO from devices as HTTP POST requests toward a user-configurable URL.
To activate or deactivate SMS MO or MT for a group of devices, you can use the toggle switches in a new or existing Service Policy to which the devices are assigned. See Service Policies for more details.
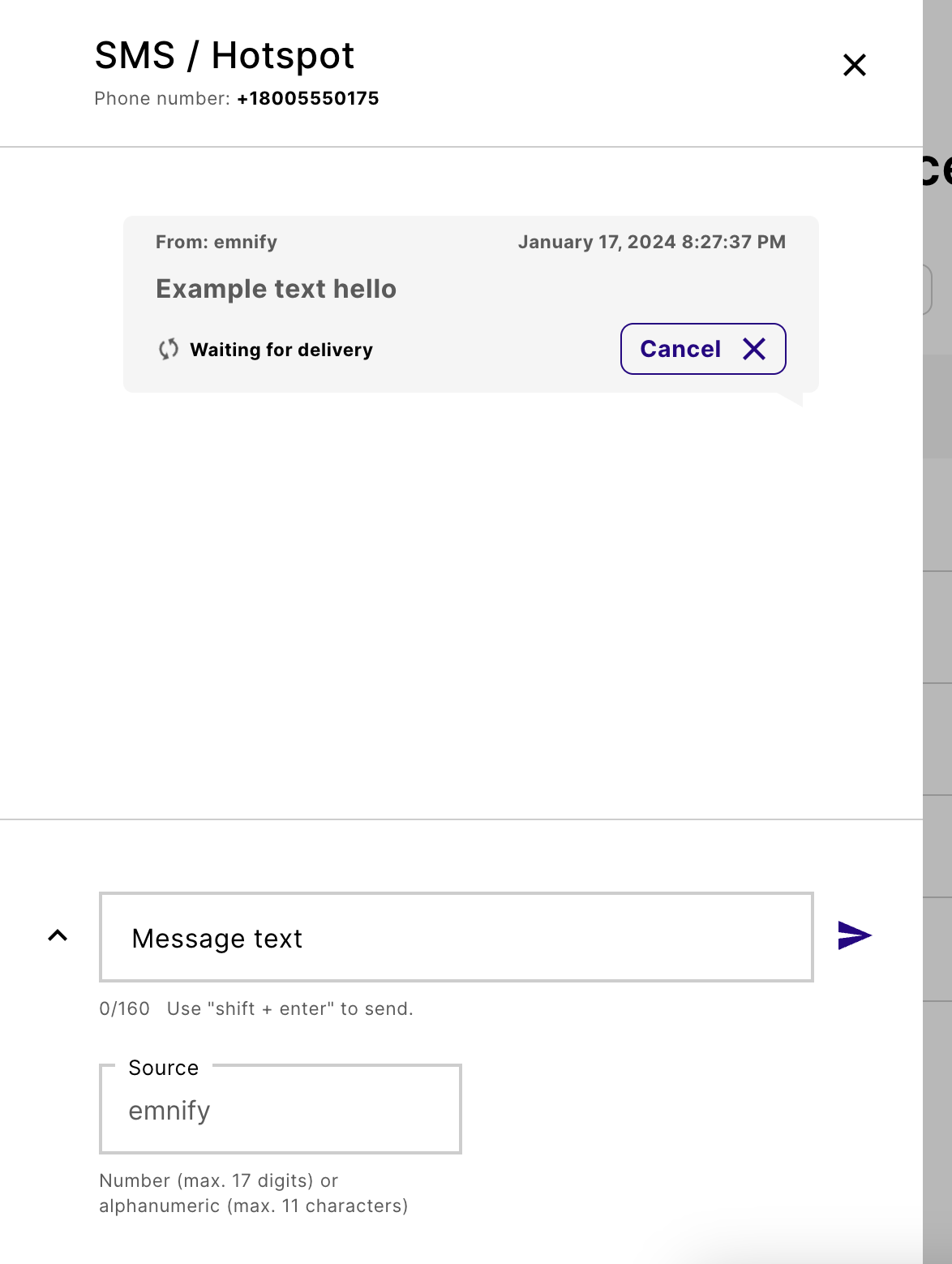
Open the SMS console
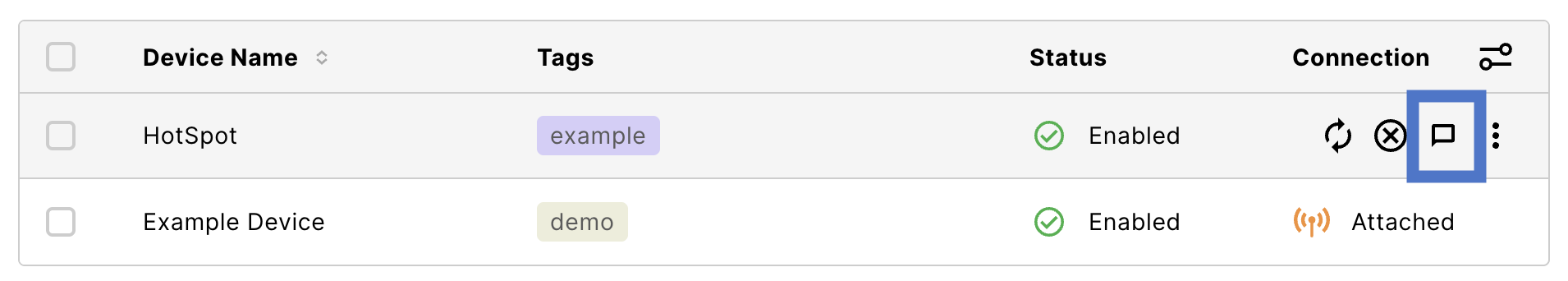
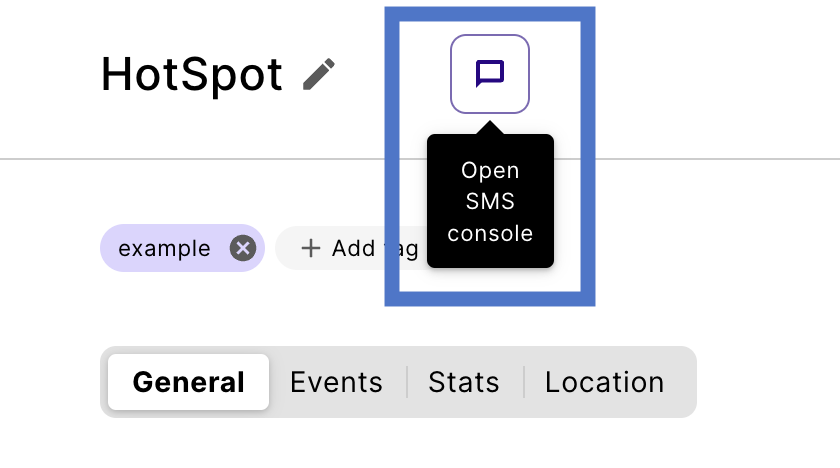
Each device has an SMS console. To open a device’s SMS console, select its message icon.
From Connected Devices
From Device Details
Show the Device SMS console